Mechanism of action for WINREVAIR (sotatercept-csrk)
WINREVAIR is the first and only activin signaling inhibitor1
Sotatercept-csrk, a recombinant activin receptor type IIA-Fc (ActRIIA-Fc) fusion protein, is an activin signaling inhibitor that binds to activin A and other TGF-β superfamily ligands
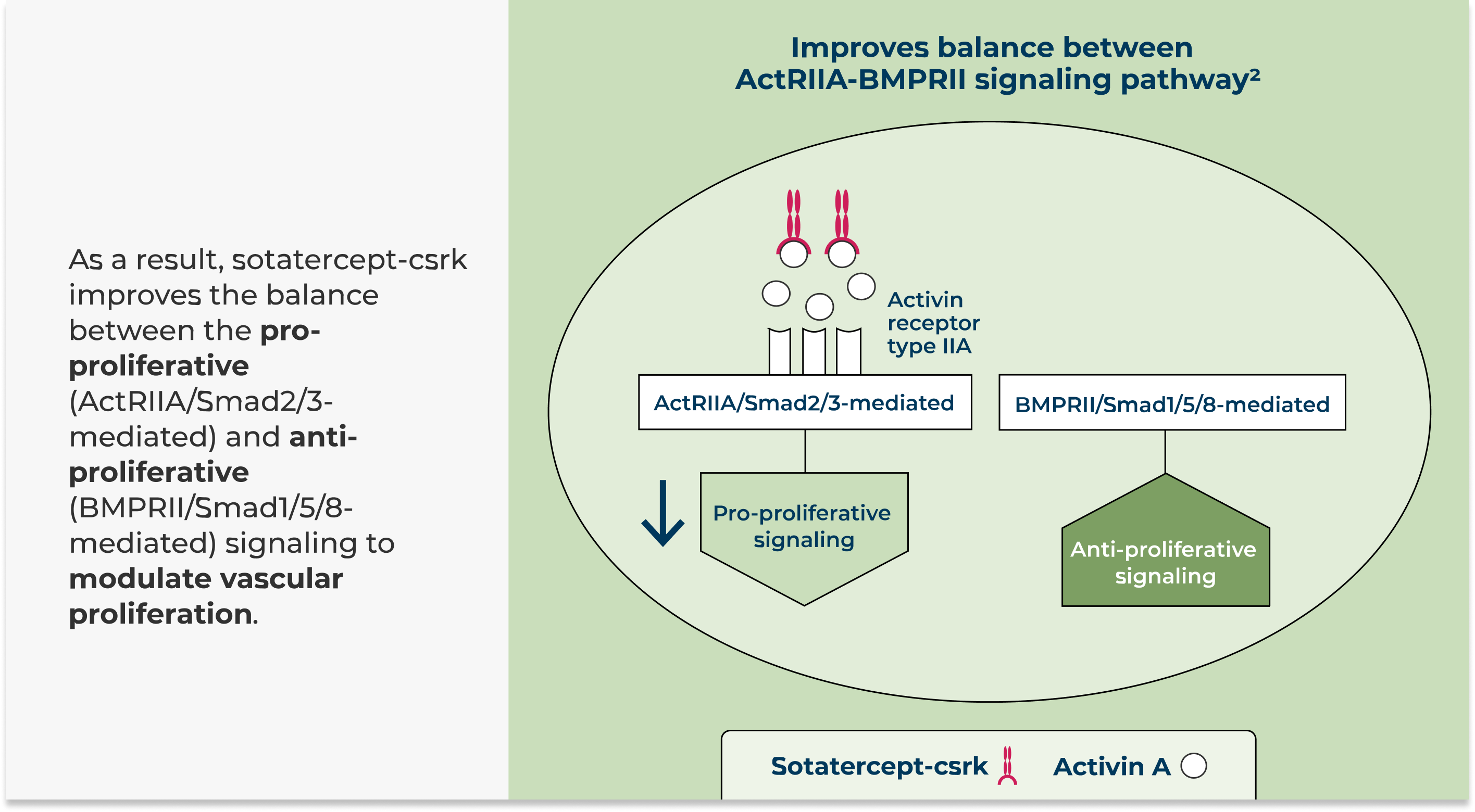
BMPRII = bone morphogenetic protein receptor type II; TGF-β= transforming growth factor beta.
In rat models of PAH, a sotatercept-csrk analog reduced inflammation and inhibited proliferation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells in diseased vasculature.
These cellular changes were associated with thinner vessel walls, partial reversal of right ventricular remodeling, and improved hemodynamics.
Mechanism of disease2,3
PAH is a condition characterized in part by vascular inflammation and excessive cell proliferation within the pulmonary arteries. These pathological changes contribute to thickened vessel walls and narrowed pulmonary arterial lumen. As a consequence, hemodynamics are compromised, and the right ventricle undergoes remodeling.
References:
- DailyMed database. Advanced search: “activin signaling inhibitor” in Mechanism of Action section. National Library of Medicine. Accessed February 10, 2025. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/advanced-search.cfm
- Humbert M, McLaughlin V, Gibbs JSR, et al. PULSAR Trial Investigators. Sotatercept for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(13):1204-1215.
- Maron BA. Pulmonary Hypertension. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, et al, eds. Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Elsevier;2022:1656-1677.
