Secondary endpoint data
In STELLAR, a 24-week study of adult patients with PAH on stable background therapy:
Significantly more patients taking WINREVAIR improved their WHO FC vs placebo1

aOne patient in the group had missing data owing to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and was excluded from the analysis.1
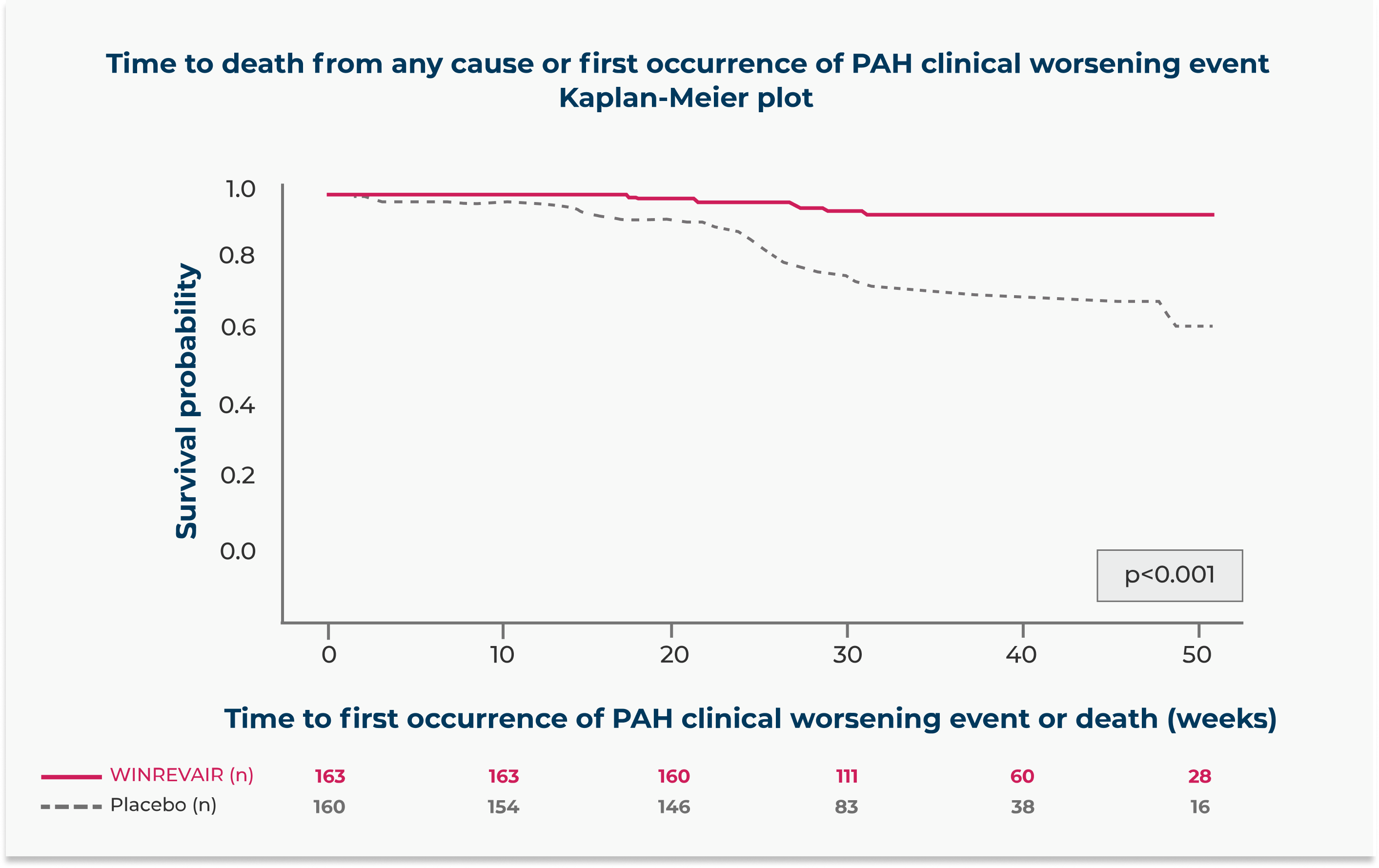
WINREVAIR significantly reduced the occurrence of death from any cause or PAH clinical worsening events vs placebo
Relative risk reduction in the occurrence of death from any cause or PAH clinical worsening events compared to placebo
(HR 0.16; 95% CI: 0.08, 0.35; p<0.001)
In the WINREVAIR group, 9 of 163 (5.5%) of patients experienced death from any cause or at least 1 PAH clinical worsening event, compared with 42 of 160 (26.3%) patients in the placebo group.
These outcomes were captured until the last patient completed the week 24 visit (data up to the data cutoff). The median duration of exposure was 33.6 weeks.
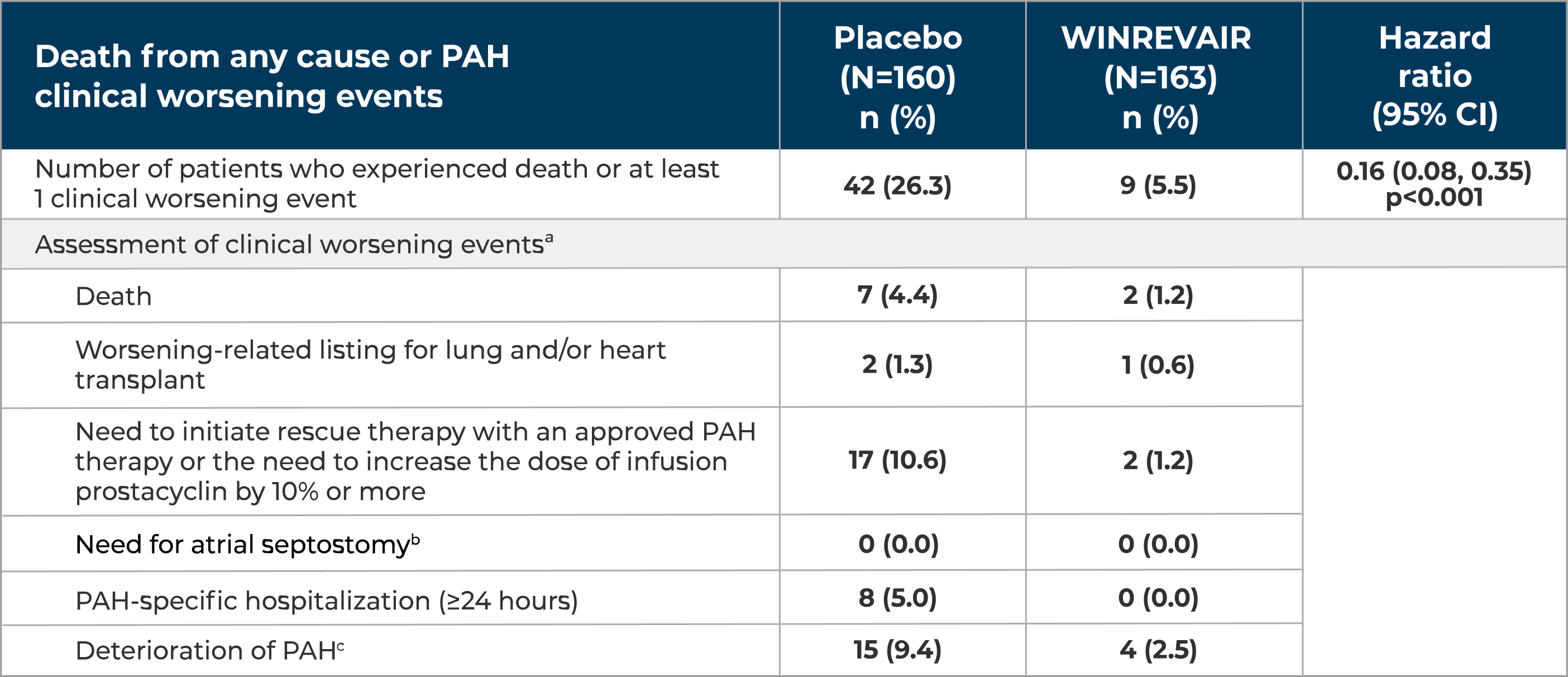
aA subject can have more than 1 assessment recorded for their clinical worsening.
bThere were no events of atrial septostomy.
cDeterioration of PAH was defined by both of the following events occurring at any time, even if they began at different times, as compared to their baseline values: (a) Worsened WHO FC (II to III, III to IV, II to IV, etc.); and (b) Decrease in 6MWD by ≥15% (confirmed by two 6MWTs at least 4 hours apart but no more than 1 week).
6MWT = 6-minute walk test; HR = hazard ratio; n = number of subjects in the category.
WINREVAIR demonstrated statistically significant decreases from baseline in PVR and NT-proBNP vs placebo
Median treatment difference between WINREVAIR and placebo at week 24
NT-proBNP = N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide; PVR = pulmonary vascular resistance.
