Efficacy of VERQUVO® (vericiguat)
In the VICTORIA study, VERQUVO® (vericiguat) plus background therapy was more effective than background therapy alone in reducing the risk of HF hospitalization and CV death in patients following a worsening HF event.
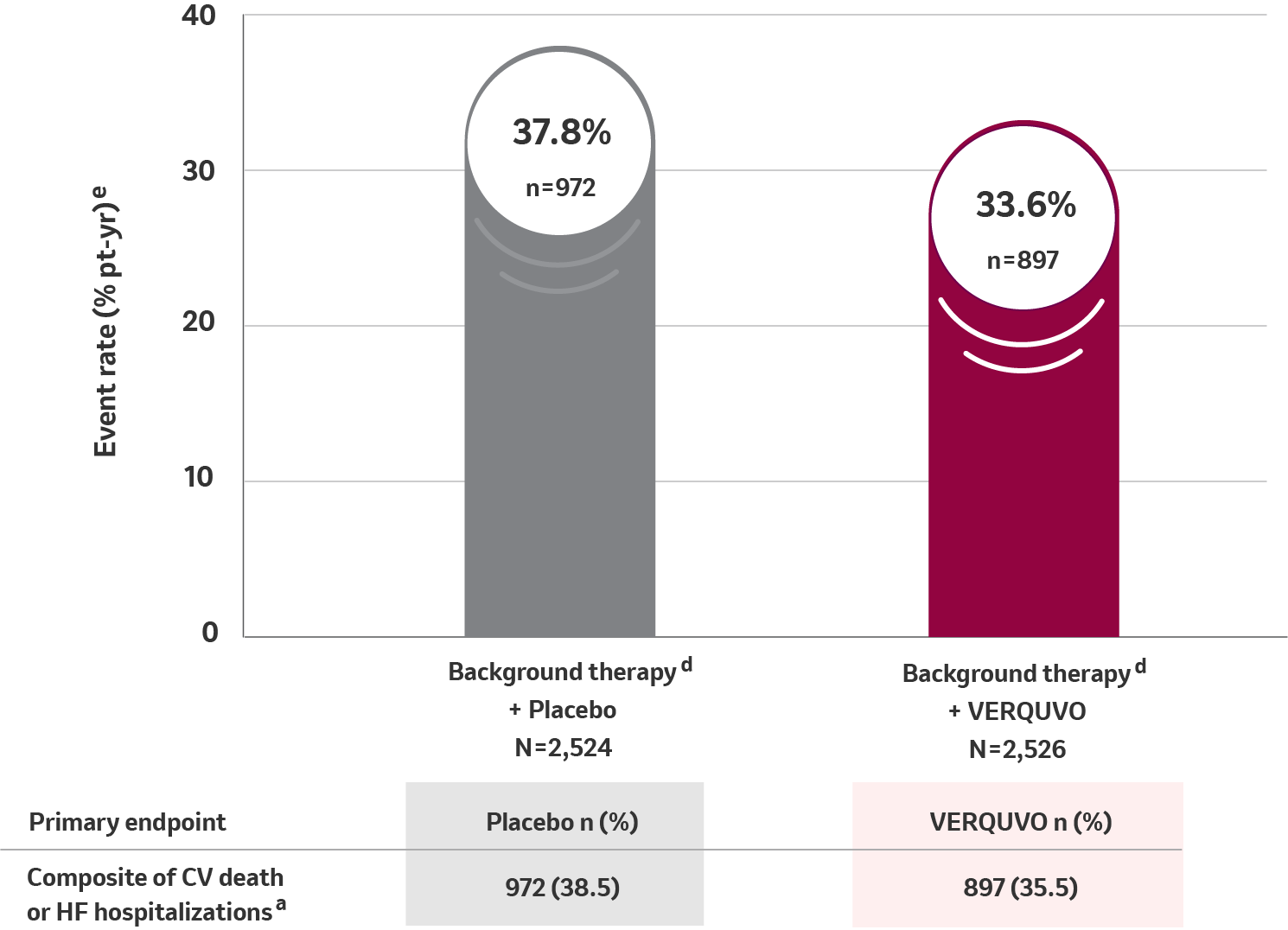
Primary composite endpoint results for CV death or HFHa
10% RRR for VERQUVO plus background therapy vs placebo plus background therapy (HR=0.90 [95% CI: 0.82−0.98] p=0.019) b,c,d
See study design below
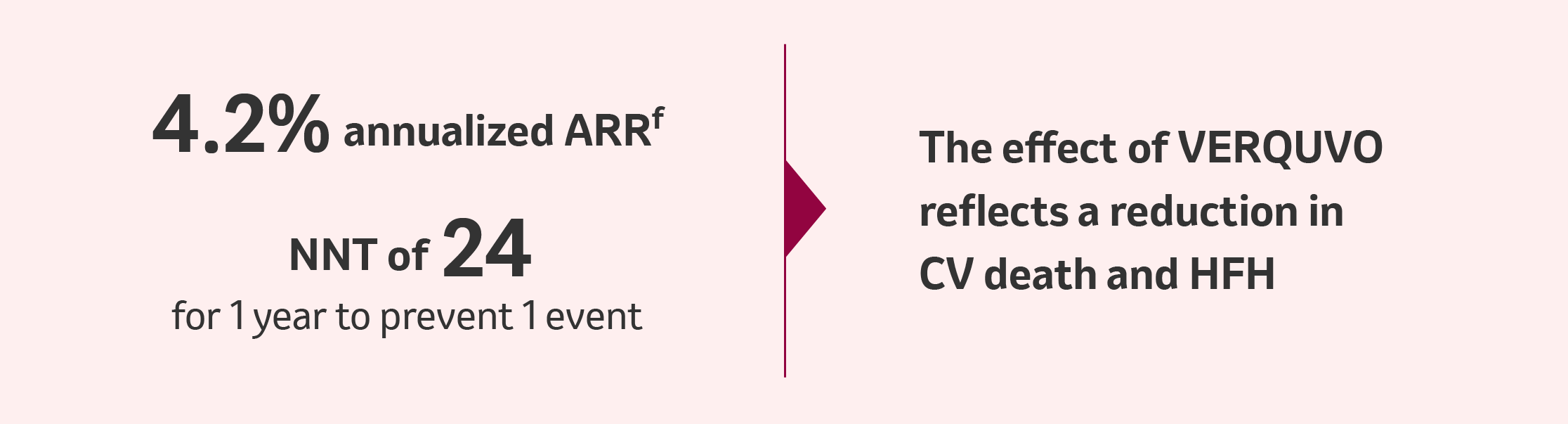
VERQUVO showed a superior annualized ARRf of 4.2% compared to placebo for cardiovascular (CV) death or HFH
aFor patients with multiple events, only the first event contributing to the composite endpoint is counted.
bHR (VERQUVO over placebo) and CI from a Cox proportional hazards model.
cFrom the log-rank test.
dBackground therapy included beta blocker, ACE inhibitor, ARB, MRA, ARNI, or SGLT2 inhibitor.
eTotal patients with an event per 100 patient years at risk.
fARR, calculated as difference (placebo – VERQUVO) in event rate per 100 patient years.
Study design
VICTORIA was a Phase 3, randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, double-blind, event-driven, multicenter trial comparing VERQUVO to placebo when added to background HF therapy in 5,050 adult patients with NYHA class II-IV chronic HF and LVEF <45% following a worsening HF event (defined as HF hospitalization within 6 months before randomization or use of outpatient IV diuretics for HF within 3 months before randomization). Patients were treated up to the target maintenance dose of VERQUVO 10 mg once daily or matching placebo. The primary endpoint was a composite of time to first event of CV death or HF hospitalization.1
Definitions:
ACE = angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB = angiotensin II receptor blocker; ARNI = combination of an angiotensin receptor and neprilysin inhibitor; ARR = absolute risk reduction; CI = confidence interval; CV = cardiovascular; HFH = heart failure hospitalization; HR = hazard ratio; LVEF = left ventricular ejection fraction; MRA = mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist; N = number of patients in Intent-to-Treat (ITT) population; n = number of patients with an event; NNT = number needed to treat; NYHA = New York Heart Association; RRR = relative risk reduction; SGLT2 = sodium glucose co-transporter 2; VICTORIA = Vericiguat in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction.
Reference:
- Armstrong PW, Pieske B, Anstrom KJ, et al. Vericiguat in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1883-1893.
