Safety
Adverse reactions of RECARBRIOTM (imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam)
Clinical trials experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Overview of the safety evaluation of RECARBRIO
Safety was primarily evaluated in three active-controlled, double-blind trials in hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP), complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI), and complicated intra-abdominal infections (cIAI) (Trials 1, 2, and 3, respectively).
In the HABP/VABP trial (Trial 1), patients were treated with either RECARBRIO™ (imipenem, cilastatin, and relebactam) or piperacillin and tazobactam (4.5 grams).
In the cUTI trial (Trial 2) and cIAI trial (Trial 3), patients in the treatment arms were treated with either imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg and relebactam 250 mg or imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg and relebactam 125 mg (not an approved dose), and patients in the control arm were treated with imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus placebo (IV normal saline). Across Trials 2 and 3, the mean duration of IV therapy in patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin plus relebactam 250 mg was approximately 7 days.
Clinical trial experience in patients with HABP/VABP
Trial 1 included 266 adult patients treated with RECARBRIO and 269 patients treated with piperacillin and tazobactam (4.5 grams) administered intravenously over 30 minutes every 6 hours. The mean age was 60 years, 43% of patients were 65 years of age and older, 31% were female and 22% had polymicrobial infection. The mean Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score was 15 and 48% of patients had an APACHE II score greater than or equal to 15 at baseline. Overall, 260 (49%) patients were ventilated at enrollment, including 194 (36%) patients with VABP and 66 (12%) patients with ventilated HABP.
Clinical trial experience in patients with cUTI including pyelonephritis
Trial 2 included 198 adult patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin and relebactam (99 patients each with imipenem 500 mg/
Clinical trial experience in patients with cIAI
Trial 3 included 233 adult patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin plus relebactam (116 subjects with imipenem 500 mg/
Serious adverse reactions and adverse reactions leading to discontinuation
In Trial 1, serious adverse reactions occurred in 27% (71/266) of patients receiving RECARBRIO and 32% (86/269) of patients receiving piperacillin and tazobactam. Adverse reactions leading to death were reported in 15% (40/266) of patients receiving RECARBRIO and 21% (57/269) of patients receiving piperacillin and tazobactam.
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation occurred in 5.6% (15/266) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg/relebactam 250 mg and 8.2% (22/269) of patients receiving piperacillin and tazobactam.
In Trials 2 and 3, serious adverse reactions occurred in 3.2% (7/216) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 250 mg and 5.1% (11/214) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg. There were no deaths reported in patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 250 mg or imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg alone. Deaths were reported in 1.4% (3/215) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 125 mg (not an approved dose).
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation occurred in 1.9% (4/216) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 250 mg and 2.3% (5/214) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg.
Common adverse reactions
In Trial 1, adverse reactions occurred during the protocol-specified follow-up period, which was IV therapy plus 14 days following completion of therapy, in 85% (226/266) of patients receiving RECARBRIO and 87% (233/269) of patients receiving piperacillin and tazobactam. The table below lists the most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥4% of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg/relebactam 250 mg or piperacillin and tazobactam in Trial 1.
Adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 4% of HABP/VABP patients receiving RECARBRIO in Trial 1
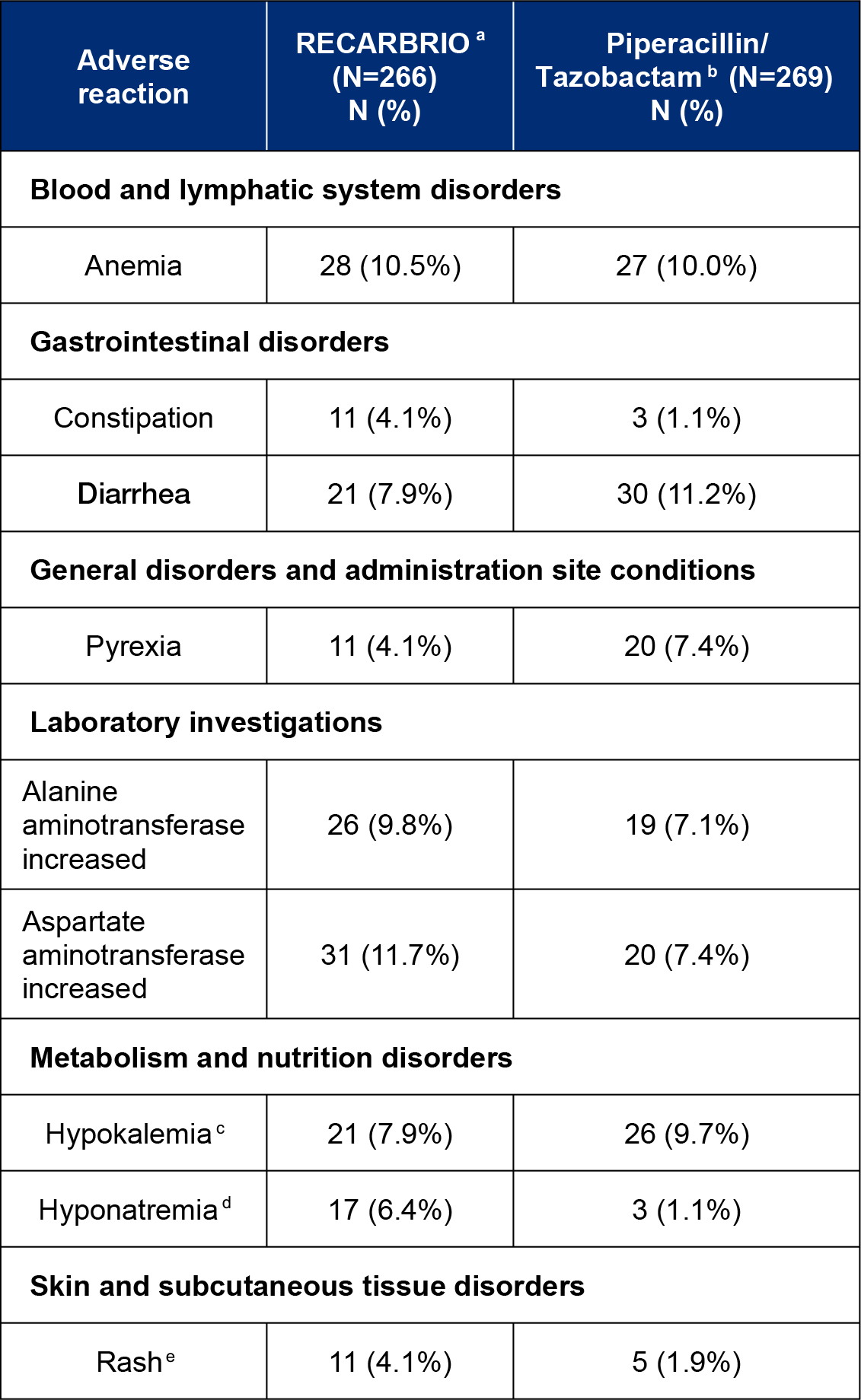
aRECARBRIO, IV every 6 hours.
bPiperacillin 4000 mg and Tazobactam 500 mg (4.5 grams), IV every 6 hours.
cHypokalemia includes hypokalemia and blood potassium decreased.
dHyponatremia includes hyponatremia and blood sodium decreased.
eRash includes rash, rash erythematous, and rash generalized.
Less common adverse reactions reported in Trial 1
The following selected adverse reaction was reported in RECARBRIO-treated subjects at a rate of less than 4%:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: thrombocytopenia
In Trials 2 and 3, adverse reactions occurred during the protocol-specified follow-up period, which was IV therapy plus 14 days following completion of therapy, in 39% (85/216) of patients receiving imipenem 500 mg/
Adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 1% of cUTI and cIAI patients receiving imipenem/cilastatin plus relebactam 250 mg or imipenem/cilastatin in Trials 2 and 3
aImipenem/Cilastatin (500 mg/500 mg) + Relebactam (250 mg), IV every 6 hours.
bImipenem/Cilastatin (500 mg/500 mg) + Placebo, IV every 6 hours.
cAnemia includes anemia and hemoglobin decreased.
dInfusion site reactions include infusion site phlebitis, infusion site erythema, and infusion site pain.
eCentral nervous system adverse reactions include agitation, apathy, confusional states, delirium, disorientation, slow speech, and somnolence.
fHypertension includes hypertension and blood pressure increased.
Other adverse reactions associated with imipenem/cilastatin
Adverse reactions reported with imipenem/cilastatin, a component of RECARBRIO, in clinical studies or during post-marketing experience are listed below. These adverse reactions are not listed above for patients treated with RECARBRIO in Trial 1 or imipenem 500 mg/cilastatin 500 mg plus relebactam 250 mg in Trials 2 and 3.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: agranulocytosis, increased eosinophils, hemolytic anemia
Nervous System Disorders: seizure
Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatic failure, jaundice
Laboratory Investigations: blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, coombs test positive, eosinophil count increased
