Mechanism of action for PREVYMIS® (letermovir)
A novel CMV DNA terminase complex inhibitor1
PREVYMIS works differently compared to other CMV prophylaxis agents
PREVYMIS acts late in the CMV replication cycle after DNA synthesis via a distinct mechanism of action2
- PREVYMIS inhibits the CMV DNA terminase complex (pUL51, pUL56, and pUL89) which is required for viral DNA processing and packaging
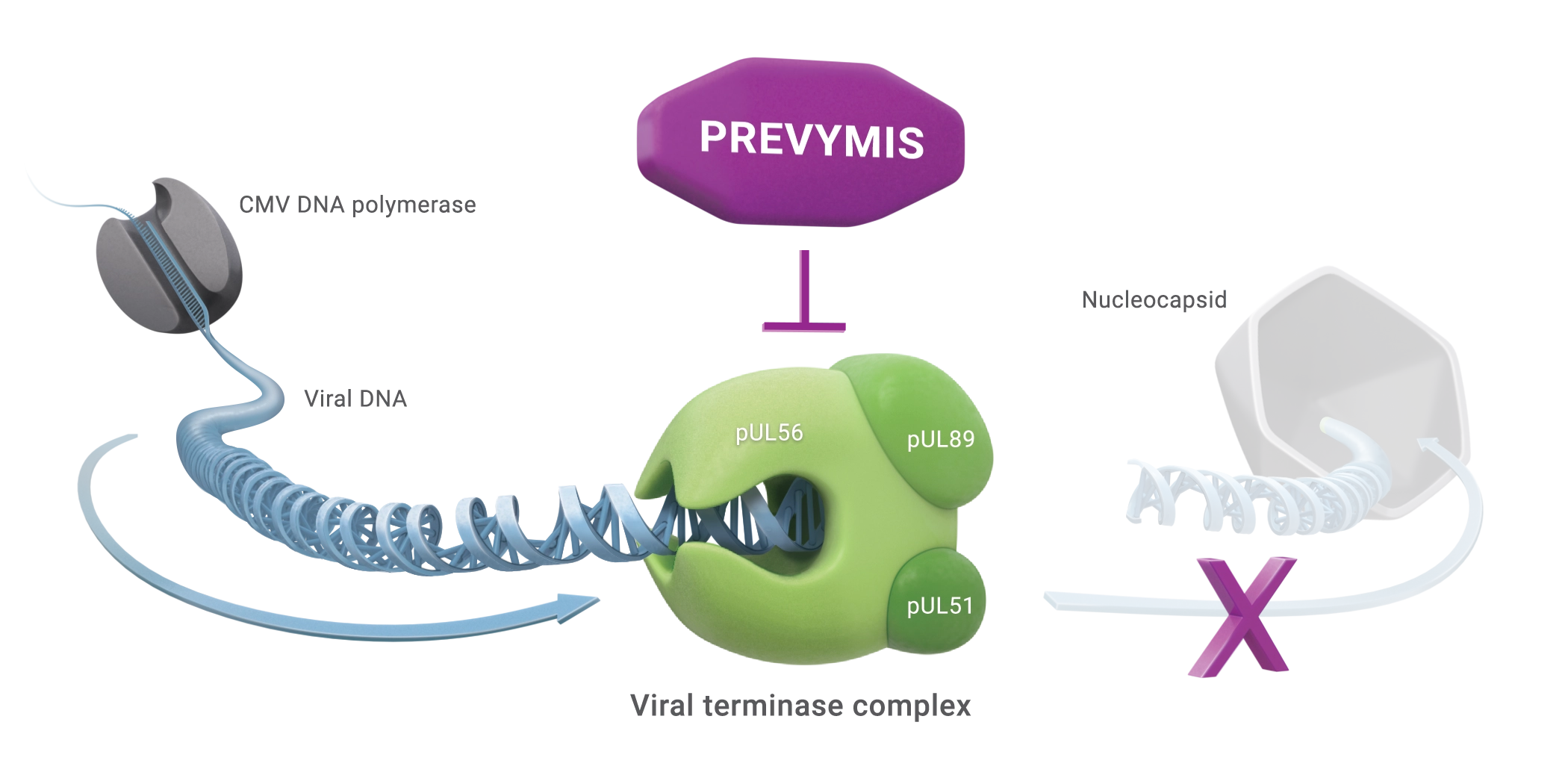
MOA of PREVYMIS in a CMV-infected human cell
Cross resistance between PREVYMIS and drugs outside of this class is unlikely
- PREVYMIS, a CMV DNA terminase complex inhibitor, is fully active against viral populations with substitutions that confer resistance to CMV DNA polymerase inhibitors (cidofovir, foscarnet, and ganciclovir)
- CMV DNA polymerase inhibitors (cidofovir, foscarnet, and ganciclovir) are expected to be fully active against viral populations with substitutions conferring resistance to PREVYMIS
References
- Razonable RR, Humar A. Cytomegalovirus in solid organ transplant recipients—guidelines of the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin Transplant. 2019;33(9):e13512. doi:10.1111/ctr.13512
- Goldner T, Hewlett G, Ettischer N, Ruebsamen-Schaeff H, Zimmermann H, Lischka P. The novel anticytomegalovirus compound AIC246 (letermovir) inhibits human cytomegalovirus replication through a specific antiviral mechanism that involves the viral terminase. J Virol. 2011;85(20):10884-10893. doi:10.1128/JVI.05265-11