Adverse events (AE) in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) patients
Safety profile through Week 14 (~100 days) post-HSCT in adults
Safety profile from Week 14 (~100 days) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT in adults
Safety profile in pediatric R+ recipients of an allogeneic HSCT
Safety profile through Week 14 (~100 days) post-HSCT in adults
Cardiac AEs
The cardiac AE rate was higher in subjects receiving PREVYMIS (13%) compared to subjects receiving placebo (6%). The most common cardiac AEs were tachycardia (reported in 4% of PREVYMIS subjects and in 2% of placebo subjects) and atrial fibrillation (reported in 3% of PREVYMIS subjects and in 1% of placebo subjects). Among those subjects who experienced 1 or more cardiac AEs, 85% of PREVYMIS and 92% of placebo subjects had events reported as mild or moderate in severity.
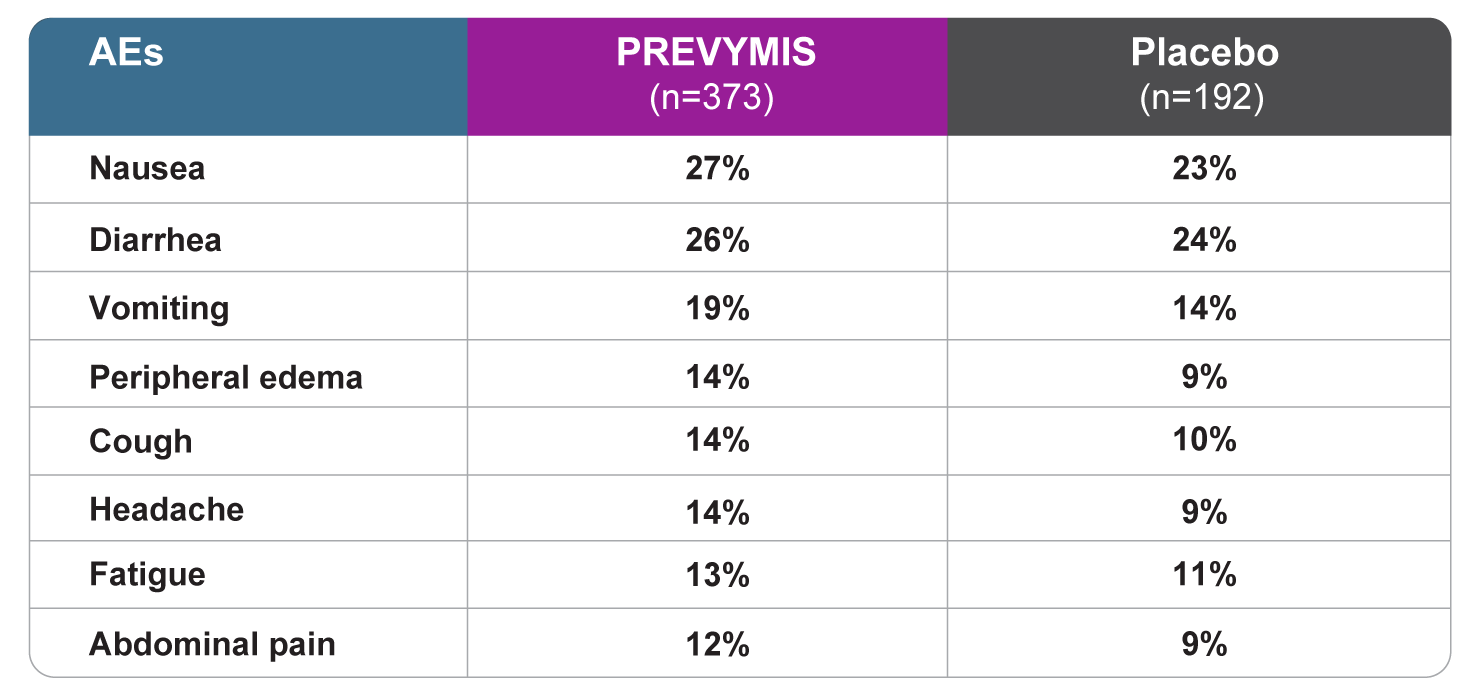
All grade AEs reported in ≥10% of patients treated with PREVYMIS at a frequency at least 2% greater than placebo
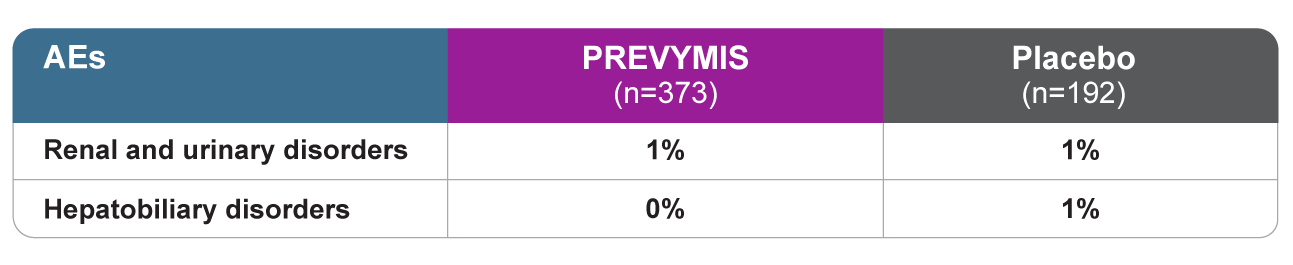
Drug-related renal and hepatic AEs1
Rates of discontinuation due to AEs were comparable between PREVYMIS and placebo (13% vs 12%, respectively).
The median time to engraftment (defined as absolute neutrophil count ≥ 500/mm3 on 3 consecutive days after transplantation) was 19 days in the PREVYMIS group and 18 days in the placebo group.
Safety profile from Week 14 (~100 days) through Week 28 (~200 days) post-HSCT in adults
- The most commonly reported adverse events with prophylaxis with PREVYMIS from Week 14 through Week 28 post-HSCT were similar to those reported with prophylaxis with PREVYMIS through Week 14 post-HSCT.
- Study drug was discontinued due to an adverse event in 5% of PREVYMIS subjects and 1% of placebo subjects.
- The cardiac adverse event rate was 4% in the PREVYMIS and placebo groups.
- The rates of hematologic laboratory abnormalities were comparable in the PREVYMIS and placebo groups. Serum creatinine abnormalities >1.5 mg/dL occurred in 15% of PREVYMIS and 8% of placebo subjects.
Safety profile in pediatric recipients of an allogeneic HSCT
The safety of PREVYMIS was evaluated in 63 pediatric subjects aged 2 months to less than 18 years of age who received an allogeneic HSCT (P030). PREVYMIS was administered orally (tablet or pellet) or intravenously. The duration of PREVYMIS exposure ranged from 3 days to 102 days (median duration 84 days).
The safety profile in pediatric patients was consistent with the safety profile observed in clinical trials of PREVYMIS in adults.
PREVYMIS is indicated for pediatric recipients of an allogeneic HSCT aged 6 months and older and weighing at least 6 kg.
References
- Data available on request from the Merck National Service Center via email at daprequests@merck.com. Please specify information package US-CYT-01957.