Dosing for PREVYMIS® (letermovir) in CMV R+ adult allogeneic HSCT patients
Once-daily dosing with PREVYMIS as early as the day of transplant
- Start PREVYMIS as early as day 0 and no later than day 28 post-transplant.
- PREVYMIS can be initiated before or after engraftment.
- Following the completion of prophylaxis with PREVYMIS, monitoring for CMV reactivation in HSCT recipients is recommended.
Adult Oral or IV dosing
In adults, the recommended dosage of PREVYMIS is 480 mg administered orally or intravenously once daily.
- If coadministered with cyclosporine, the recommended dose of PREVYMIS is 240 mg once daily.
- Please see full Prescribing Information for proper preparation and administration of PREVYMIS IV infusion.
- PREVYMIS injection should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy and patients should be switched to oral PREVYMIS as soon as they are able to take oral medications. If possible, intravenous administration should not exceed 4 weeks.
- No dosage adjustment is necessary when switching formulations in adults.
Once-daily dosing
Dosage forms
PREVYMIS Tablets
- Administer orally with or without food.
- Swallow tablets whole.
PREVYMIS Injection
- PREVYMIS injection must be diluted prior to administration.
- Administer PREVYMIS through a sterile 0.2 micron or 0.22 micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter.
- Administer by intravenous infusion via a peripheral catheter or central venous line at a constant rate over 1 hour.
- Do not administer as an intravenous bolus injection.
- PREVYMIS injection, which contains hydroxypropyl betadex, should be used only in patients unable to take oral therapy. Patients should be switched to oral PREVYMIS as soon as they are able to take oral medications. If possible, intravenous administration should not exceed 4 weeks.
- In patients with renal impairment, accumulation of hydroxypropyl betadex may occur. In adult patients with CLcr less than 50 mL/min, closely monitor serum creatinine levels.
- Animal studies have shown the potential for hydroxypropyl betadex to cause ototoxicity. The active ingredient, letermovir, is not known to be associated with ototoxicity.
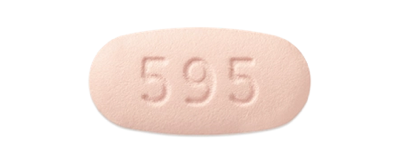
480 mg tablet
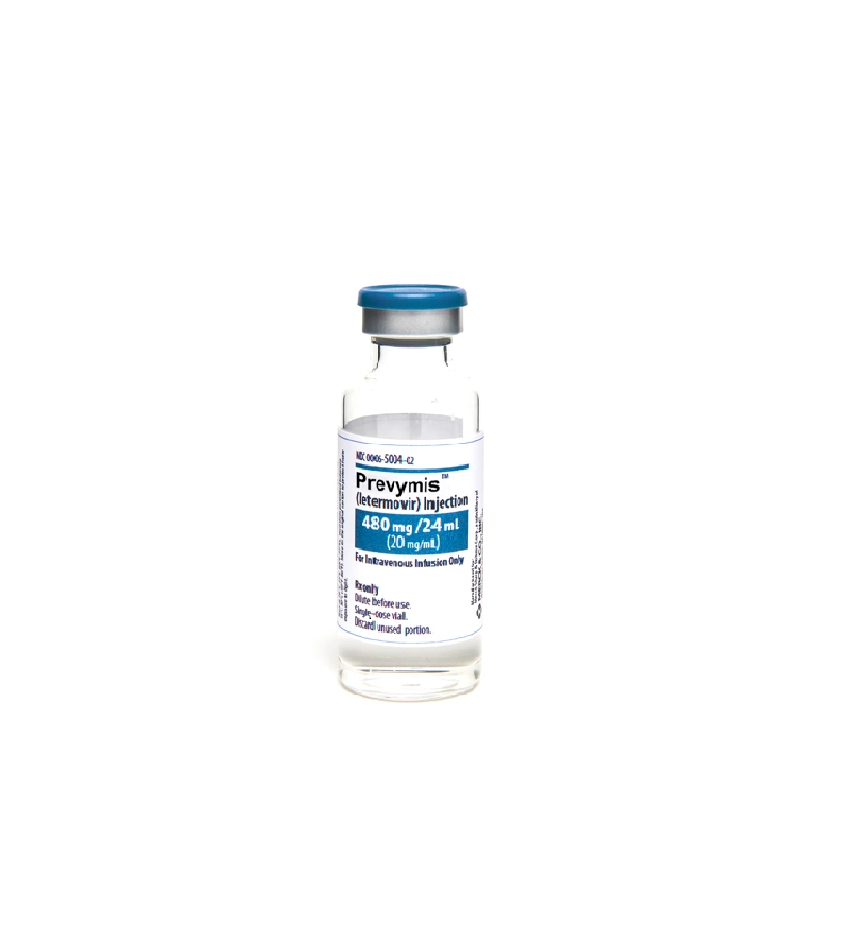
480 mg/24 mL vial

240 mg tablet
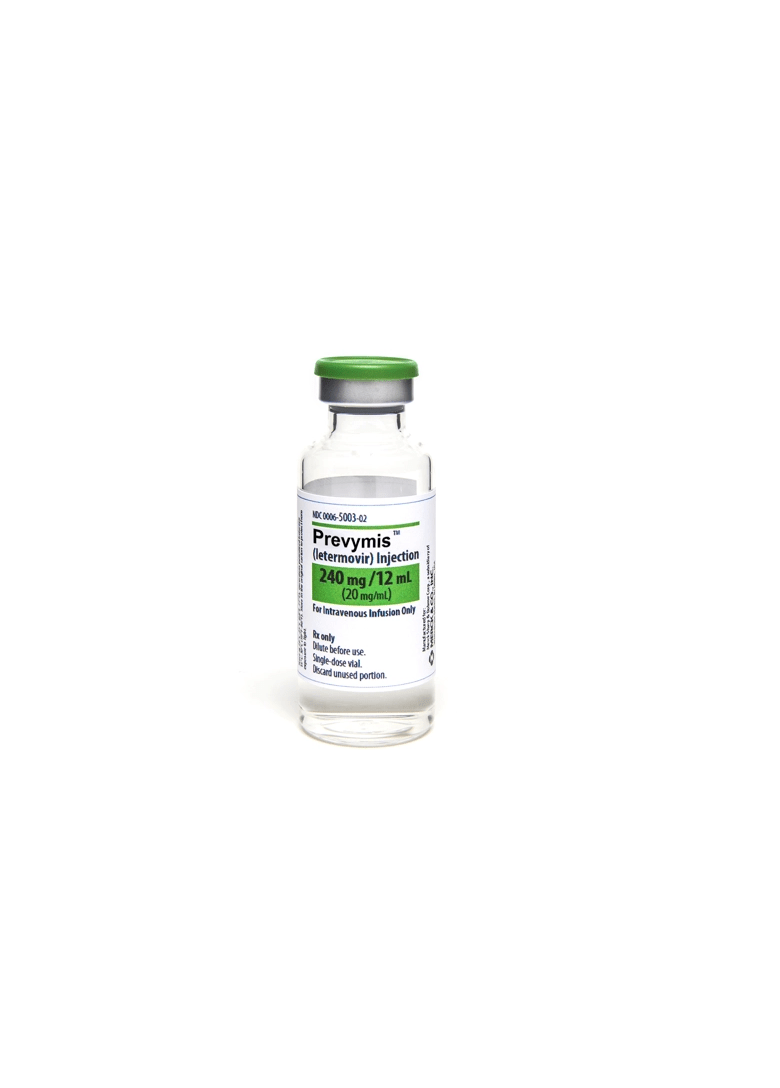
240 mg/12 mL vial
Tablets and vials not actual size.